Lean manufacturing makes use of various lean tools for improvement in production effectiveness and efficiency. The main goal of such an approach is to get the maximum output by making use of less time, less effort and fewer resources, that is, to create a Lean process. Continual improvement is an important part of every operation and the same can be achieved by applying the lean tools. Some of the commonly used Lean tools in manufacturing are as follows:
- Kaizen
- Poka-Yoke
- Jidoka
- Gemba
- Kanban
- Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED)
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
In continuation our series, this article discuss about Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) in detail:
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
TPM is a system of maintaining and improving the integrity of production, safety and quality systems through the machines, equipment, processes and employees that add business value to an organization. It can lead to reduced loss due to equipment failure by keeping the buffer stock zero or minimum. Involvement of everyone in the organization is required for the maintenance process. Following are the objectives of the Total Productive Maintenance:
- Ensure equipment reliability
- Develop maintenance skills
- Assure maximum equipment efficiency
- Optimize cost of quality related to machines
- Prevent unplanned machine downtime
- Perform efficient maintenance staff management
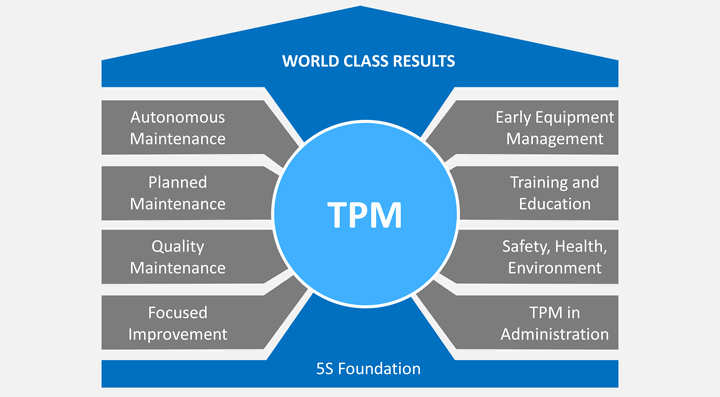
The 8 Pillars of TPM can be described as follows:

TPM measures how effectively the equipment is being used. It is a proactive approach to maximize the operational efficiency of the equipment. The overall productivity is increased by reduction in downtime.

.png
)