As per ICH Q9 “Quality Risk Management is a systematic process for the assessment, control, communication and review of risks to the quality of the product throughout its life cycle.” There are many methods and tools to perform Quality Risk Management. It is important to understand that none of the tool or set of tools are sufficient to address every situation of Quality Risk Management. Some of the important tools are as follows:
- Basic Risk Management Facilitation Methods
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Failure Mode, Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA)
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)
- Hazard Operability Analysis (HAZOP)
- Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA)
- Risk Ranking and Filtering
- Supporting Quality and Statistical Tools
In this article we shall be discussing about one of the most important tool i.e. Fault Tree Analysis.
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a quality technique which makes use of a tree diagram for studying the distinct failure and checking the reliability of a process, product or system. It is a deductive, top down failure analysis approach which analyzes the system with use of sequential logic combined with a series of lower level events. FTA is an extensively used method for system reliability, safety and maintainability analysis. This tool evaluates system (or sub-system) failures one at a time but can combine multiple causes of failure by identifying causal chains. The results are represented pictorially in the form of a tree of fault modes.
Component level failures are the basic events and the system level failure are the top events which occurs in a system. FTA is used for determining the failure which has already happened or any potential failure which may happen. The two main elements of FTA are Event gates and Logic gates which links the events to find the root cause of any undesirable event.
Knowing the probabilities of every cause can lead to calculation of the real probability of failure which can be determined from the FTA. Fault tree analysis is primarily to recognize the undesirable changes which can be eliminated or minimized for reducing the chances of failure. It is mainly used in industries where even a single failure can lead to huge consequences.
Compared to Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), FTA is a less complicated method. FTA focuses on the possibility of system failures arising from undesired top events whereas in FMEA analysis of every possible failure mode are conducted regardless of their rate of severity.
FTA can be used to assess the risk level of all system types by identifying all the possible causes and mitigating the same before it can occur. Following are some areas where FTA can be used:
- Designing or redesigning of a system, product, service or process
- Identifying potential cause of failure and preventing it to occur
- To identify cause of an error or accident and to prevent its occurrence in future
- To identify failure in complicated system where multiple interrelated failures are present
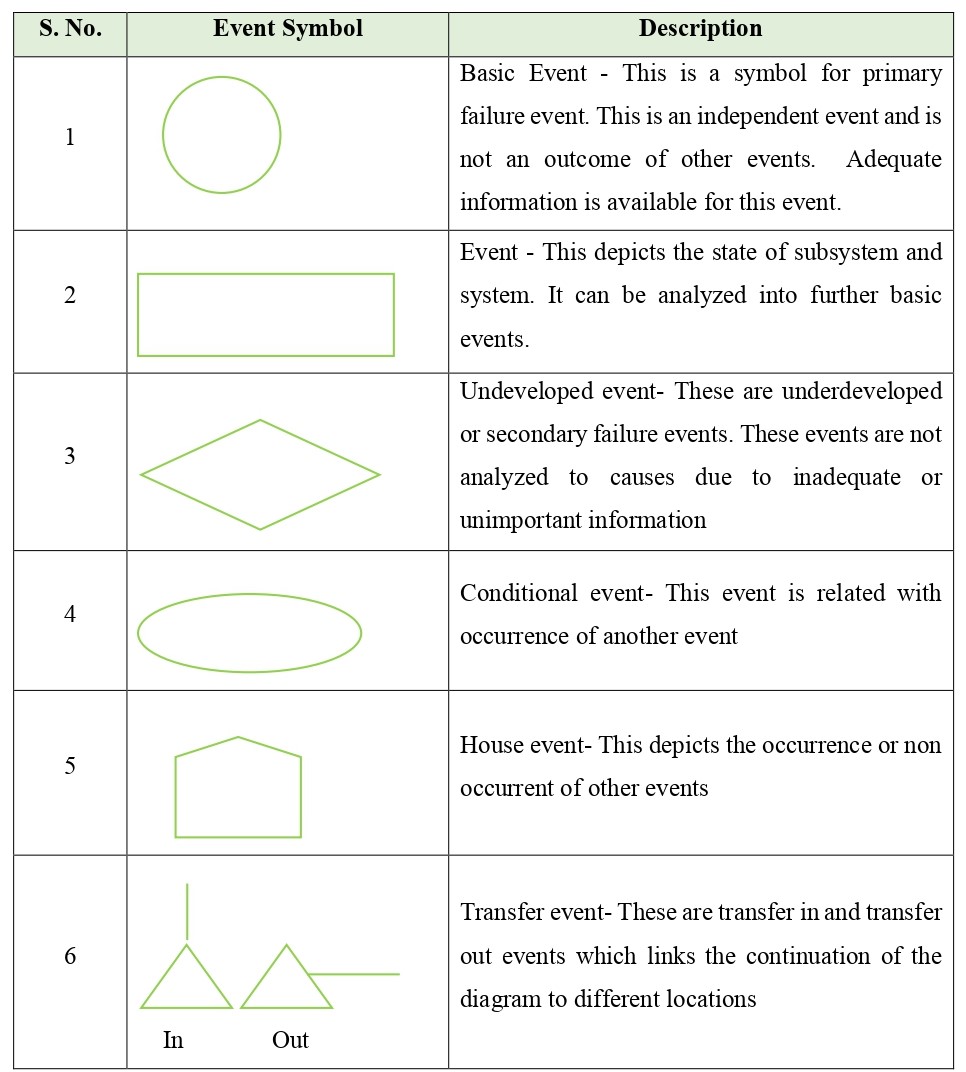
Event Symbols of the Fault Tree Analysis are as follows:
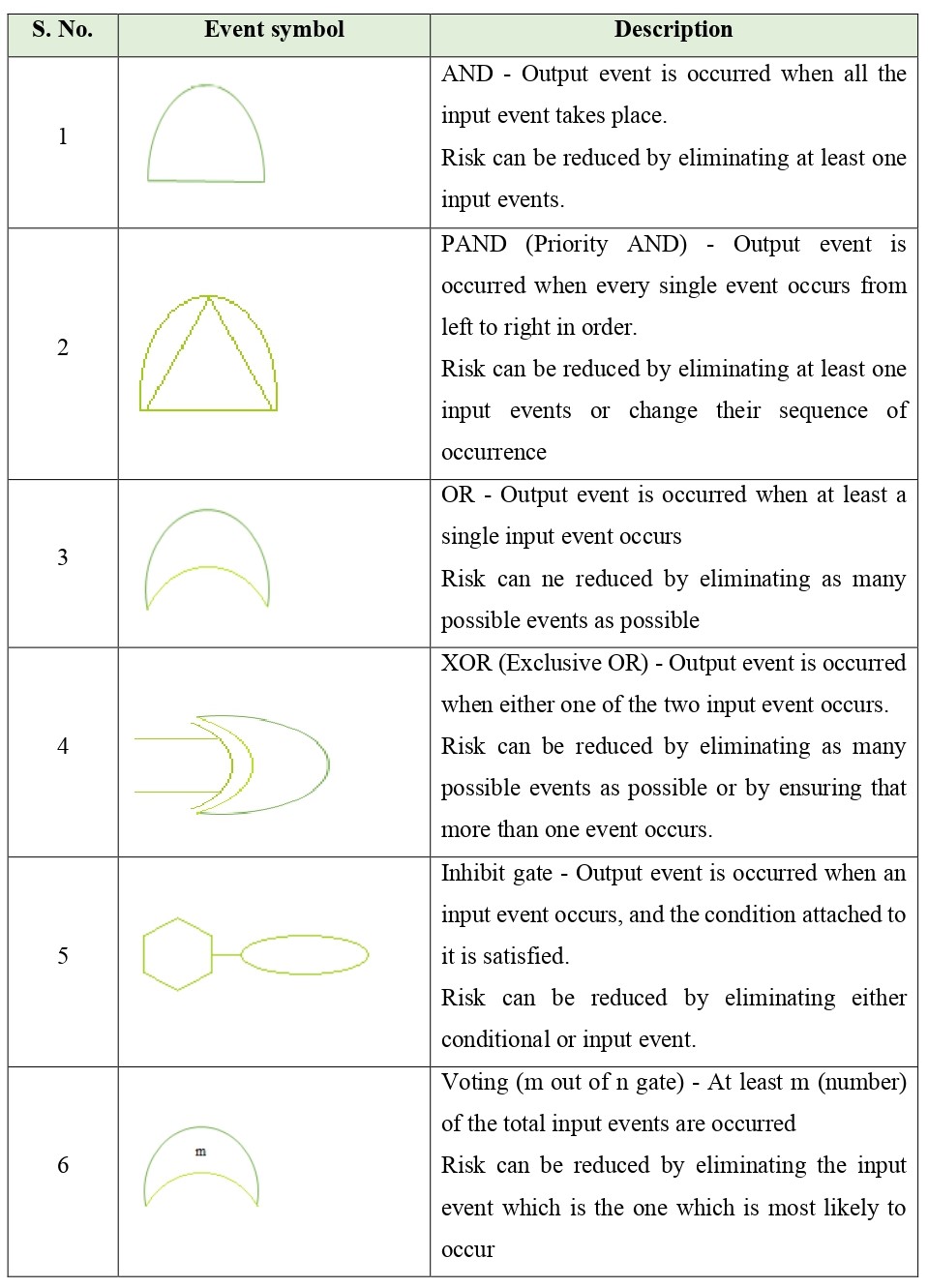
Gate Symbols used in Fault Tree Analysis are as follows:
Procedure for carrying out Fault Tree Analysis:
- Identify the process or system to be examined with its boundaries
- Identify the failure type to be analysed as narrow as possible which is the Top Event. Draw the Event symbol (rectangular box) at the top to initiate the diagram and write the failure description in it
- Identify the immediate causes for the top event and write them below the event they cause
- For the events, if it is a basic failure then draw circle around, if its own causes can be analysed then draw rectangle around it, and so on draw appropriate symbols which are defining the event
- Gate symbols are used to indicate the relationship between the events. Lower level events depict the Input events and their causes are the Output event
- Step 3, 4 and 5 are repeated for all the steps that are not basic. This is repeated till all the events end in an undeveloped or basic event
- Probabilities are assigned to every basic event to determine their probability of failure mathematically
- The FTA is analysed to study the relationship between the causes leading to events and ways to overcome them to prevent further appearance. Probability of the lowest level events and bottom up probabilities are calculated. This can help in reducing the risk.
Example of Fault tree analysis for a truck accident:
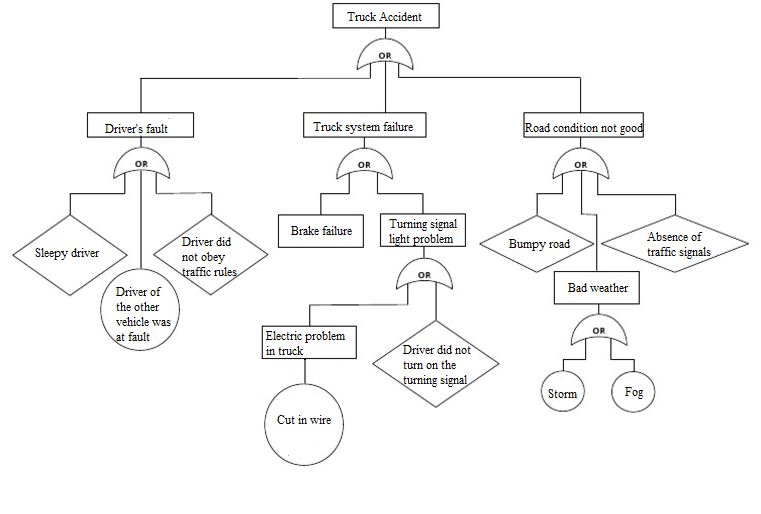
FTA is used to establish the pathway to the root cause of the failure. FTA can be used to investigate complaints or deviations in order to fully understand their root cause and to ensure that intended improvements will fully resolve the issue and not lead to other issues. Fault Tree Analysis is an effective tool for evaluating how multiple factors affect a given issue. It is useful both for risk assessment and in developing monitoring programs
Fault Tree Analysis has certain advantages as follows:
- It provides visual appearance of the events leading to failure and thus can be reduced by working upon
- System can be analyzed efficiently and quickly
- Helpful in prioritizing of the issues leading to failure which makes the problem-solving task easier
- System failure components can be highlighted
- Gives quantitative and qualitative analysis of the system
- Helps in generating foundation for future analysis and evaluation
Although, Fault Tree Analysis has numerous advantages which can lead to efficient process, but it has certain disadvantages as well which are listed as follows:
- It examines one top event only
- Time related factors causing delays are difficult to capture
- It becomes an extensive system due to the presence of several gates and events
- Logical gate understanding is not easy and has to be performed by experienced personnel only
From the advantages and disadvantages listed above, it is evident that the advantages outweigh the disadvantages. With proper planning and understanding, Fault Tree Analysis can yield beneficial results in the long run.
Reference: ICH Q9 Quality Risk Management

.png
)
